Drug Delivery and Immunomodulation
Drug delivery is a multifaceted field dedicated to improving therapeutic outcomes by altering the course and final destination of therapeutics in the body. Vehicles such as liposomes, hydrogels, and dendrimers are just a handful of ways used to improve drug targeting and reduce adverse effects. Our laboratory primarily focuses on utilizing drug delivery for immunomodulation, which is the process of altering immune responses. One example is research published by our lab on itaconate delivery.
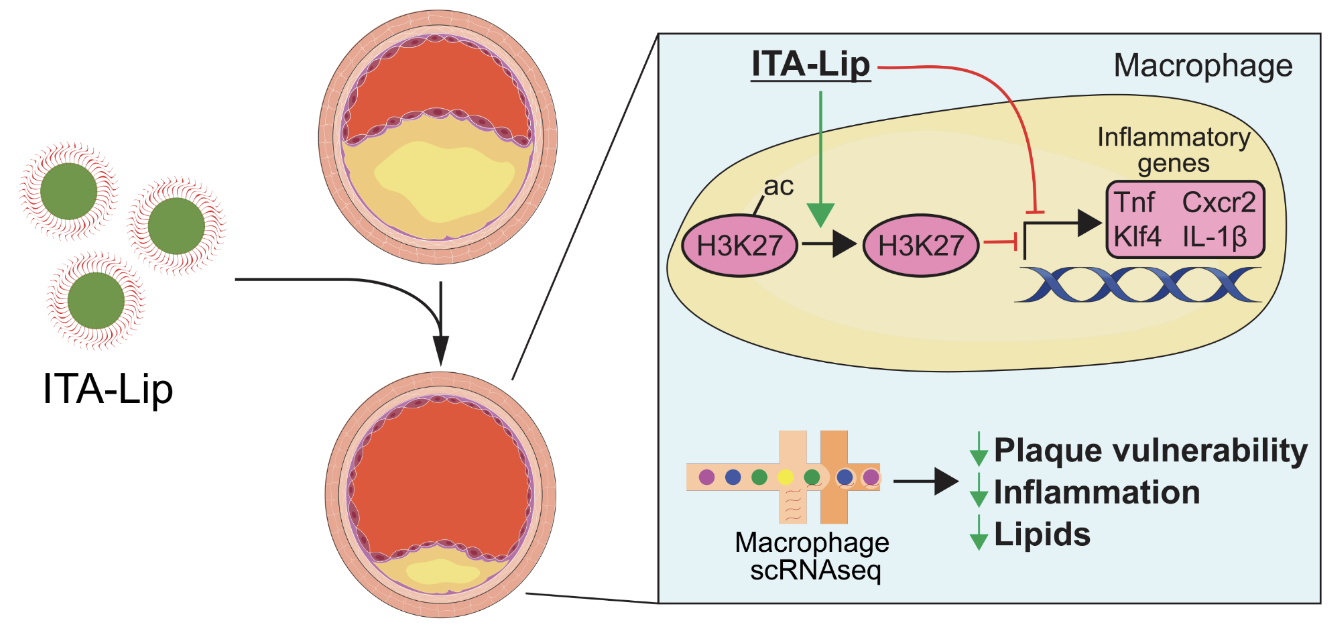
Itaconate is a tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle product that has recently come to the forefront of immunomodulation research. It is produced by activated macrophages and has been shown to regulate inflammation via a number of different mechanisms, including activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and epigenetic regulation via histone deacetylation. Because it is able to regulate inflammation without negatively suppressing the immune system, itaconate and its derivatives have been widely studied in many models of inflammation, such as atherosclerosis, sepsis, and Alzheimer’s.
Itaconate is a molecule with great promise, but it is limited as a therapeutic by its polar structure, making it difficult to cross the cell membrane and requiring high concentrations of itaconate to achieve noticeable effects. While itaconic derivatives (e.g., 4-octyl-itaconate) greatly increase the bioavailability of itaconate, they have also been reported to have different effects from endogenous itaconate and are not known to improve targeting efficacy of itaconate.
We leverage lipid nanoparticles to solve this problem by conjugating itaconate to the nanoparticles (ITA-LNPs). The formation of particles increases selective uptake by myeloid cells (e.g., macrophages), improving therapeutic outcomes in diseases that are heavily affected by myeloid cell inflammation, such as atherosclerosis. Additionally, ITA-LNPs release unconjugated itaconate intracellularly, which allow us to study the effects of endogenous itaconate in disease models by recapitulating the immunomodulatory effects unique to unmodified itaconate.
citation: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124724012622
We Published These!
- Bagalkot V, Deiuliis JA, Rajagopalan S, Maiseyeu A. “Eat me” imaging and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Apr 1;99(Pt A):2-11.
- Di L, Maiseyeu A. Low-density lipoprotein nanomedicines: mechanisms of targeting, biology, and theranostic potential. Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):408-421.
- Switala L, Di L, Gao H, Asase C, Klos M, Rengasamy P, Fedyukina D, Maiseyeu A. Engineered nanoparticles promote cardiac tropism of AAV vectors. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 3;22(1):223.
- Mog B, Asase C, Chaplin A, Gao H, Rajagopalan S, Maiseyeu A. Nano-Antagonist Alleviates Inflammation and Allows for MRI of Atherosclerosis. Nanotheranostics. 2019 Nov 1;3(4):342-355.
- Maiseyeu A. Non-antigenic regulators of targeting for imaging and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Apr 1;99(Pt A):1.
- Bagalkot V, Badgeley MA, Kampfrath T, Deiuliis JA, Rajagopalan S, Maiseyeu A. Hybrid nanoparticles improve targeting to inflammatory macrophages through phagocytic signals. J Control Release. 2015 Nov 10;217:243-55.
- Maiseyeu A, Badgeley MA, Kampfrath T, Mihai G, Deiuliis JA, Liu C, Sun Q, Parthasarathy S, Simon DI, Croce K, Rajagopalan S. In vivo targeting of inflammation-associated myeloid-related protein 8/14 via gadolinium immunonanoparticles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Apr;32(4):962-70.